Histogram Equalization
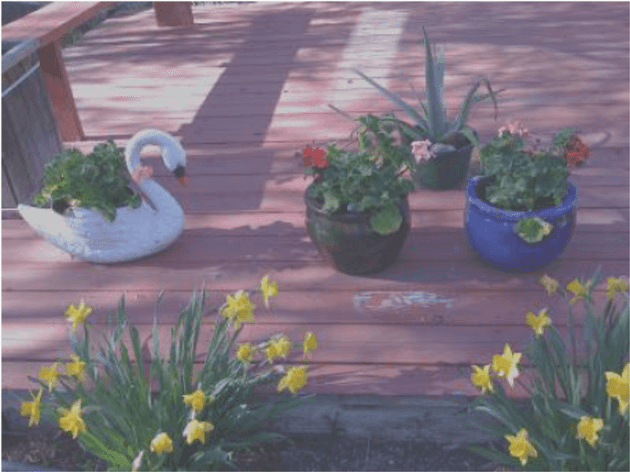
The original image:
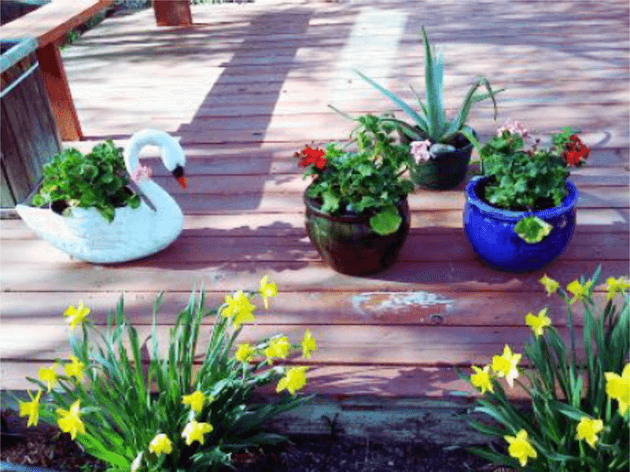
The modified color image after applying the histogram equalization algorithm to R, G, and B channels separately
Java Solution:
import java.io.*;
public class P1 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try { in = new
FileInputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/summer_deck2.raw");
out = new
FileOutputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/summer_deck2+.raw");
int i, j, k;
int[][][] image_in = new int[3][400][300];
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++)
image_in[k][i][j] = in .read(); // Read the input image into
// image_in[][][]
int[][][] image_out = new int[3][400][300]; // 3 is three channels for red, green and blue
int[] h = new int[256];
int[] H = new int[256];
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) // initialization of h[]
h[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++)
h[image_in[k][i][j]]++;
H[0] = h[0];
for (i = 1; i < 256; i++) // Compute the cumulative histogram and
// store it in H[]
H[i] = H[i - 1] + h[i];
double s = 0.002125; // get the scaling factor S
// 0.00213 is k-1/m*n which is 255(8 bits grayscale per
channel) / 400 * 300
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) // Normalize H[] with the scaling factor S
H[i] *= s;
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++) // get the image_out[] from the H[]
image_out[k][i][j] = H[image_in[k][i][j]];
}
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++)
out.write(image_out[k][i][j]);
} finally {
if ( in != null) { in .close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}
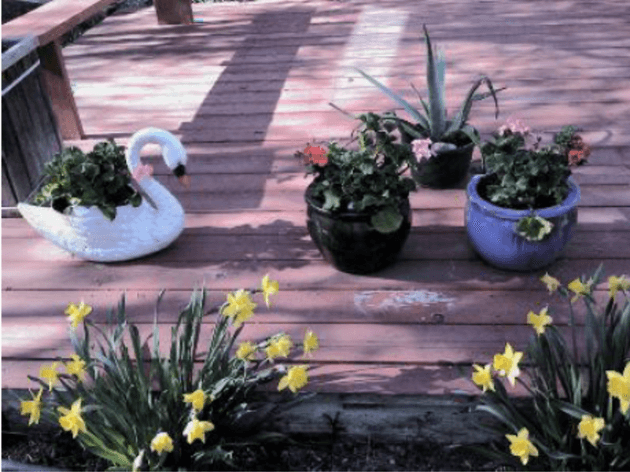
Transfer the original image from GRB model to HSV model. Applying the histogram equalization to v which is the value in HSV. Transfer the processed HSV color image back to GRB model.
Java Solution
import java.io.*;
public class P2 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try { in = new
FileInputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/summer_deck2.raw");
out = new
FileOutputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/summer_deck2++.raw");
int i, j, k;
int[][][] image_in = new int[3][400][300];
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++)
image_in[k][i][j] = in .read();
int[][][] image_out = new int[3][400][300];
channels
for red, green and blue
double[][][] hsv = new double[3][400][300];
// RGB to HSV
int r, g, b;
double rr, gg, bb;
double h = 0, s, v;
double min, max, delta;
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++) {
// do the calculation according to the mathematical formula
r = image_in[0][i][j];
g = image_in[1][i][j];
b = image_in[2][i][j];
rr = r / 255.0;
gg = g / 255.0;
bb = b / 255.0;
min = Math.min(Math.min(rr, gg), bb);
max = Math.max(Math.max(rr, gg), bb);
delta = max - min;
// get V
v = max;
// get S
if (max != 0)
s = delta / max;
else {
s = 0;
h = -1;
}
// get H
if (rr == max)
h = (gg - bb) / delta;
if (gg == max)
h = 2 + (bb - rr) / delta;
if (bb == max)
h = 4 + (rr - gg) / delta;
h *= 60;
if (h < 0)
h += 360;
hsv[0][i][j] = h;
hsv[1][i][j] = s;
hsv[2][i][j] = v;
}
// histogram equalization of values (v)
int[] hh = new int[256];
int[] H = new int[256];
int vvv;
// initialization of h[]
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
hh[i] = 0;
// Compute the histogram of values and store it in h[]
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++) {
vvv = (int)(hsv[2][i][j] * 255.0);
hh[vvv] += 1;
}
// Compute the cumulative histogram and store it in H[]
H[0] = hh[0];
for (i = 1; i < 256; i++)
H[i] = H[i - 1] + hh[i];
// get the scaling factor S 0.002 is k-1/m*n which is
255 / 400 * 300
double ss = 0.002;
// Normalize H[] with the scaling factor S
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
H[i] *= ss;
// get the processed values array from the H[]
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++) {
vvv = (int)(hsv[2][i][j] * 255.0);
hsv[2][i][j] = H[vvv] / 255.0;
}
// HSV to RGB
rr = 0;
gg = 0;
bb = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++) {
h = hsv[0][i][j];
s = hsv[1][i][j];
v = hsv[2][i][j];
double c, x, m;
// do the calculation according to the
mathematical formula
c = (v * s);
x = c * (1 - Math.abs((h / 60) % 2 - 1));
m = v - c;
if (h >= 0 && h < 60) {
rr = c;
gg = x;
bb = 0;
}
if (h >= 60 && h < 120) {
rr = x;
gg = c;
bb = 0;
}
if (h >= 120 && h < 180) {
rr = 0;
gg = c;
bb = x;
}
if (h >= 180 && h < 240) {
rr = 0;
gg = x;
bb = c;
}
if (h >= 240 && h < 300) {
rr = x;
gg = 0;
bb = c;
}
if (h >= 300 && h < 360) {
rr = c;
gg = 0;
bb = x;
}
r = (int)((rr + m) * 255.0);
g = (int)((gg + m) * 255.0);
b = (int)((bb + m) * 255.0);
image_out[0][i][j] = r;
image_out[1][i][j] = g;
image_out[2][i][j] = b;
}
// Write the result image_out[][]
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 400; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 300; j++)
out.write(image_out[k][i][j]);
} finally {
if ( in != null) { in .close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}Pseudo Color
The original image:
The processed image by applying the pseudo color:
Java Solution
import java.io.*;
public class P3 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try { in = new FileInputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/tempusa.raw");
out = new
FileOutputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/tempusa+.raw");
int i, j, k;
int[][] image_in = new int[640][420];
for (i = 0; i < 640; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 420; j++)
image_in[i][j] = in .read(); // Read the input image into
image_in[][]
int[][][] image_out = new int[3][640][420]; // 3 is three channels for red, green and blue
int[][] table = new int[256][3]; // generate a pseudo color look-up table
with 256 entries
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) // the initialization of the pseudo color look-up
table
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
table[i][j] = 0;
table[0][0] = 255; // set red
table[85][1] = 255; // set green
table[170][2] = 255; // set blue
// the pseudo color look-up table is a loop from red to green to blue and
back
// to blue
// for the grayscale is from 0 to 255, I set the step is 3 in this pseudo
color
// table
// from [255][0][0] , [252][3][0] , [249][6][0] ... to [0][255][0] and from
// [0][255][0] , [0][249][3] , [0][246][6] to [0][0][255] and then back to
// [255][0][0]
// generate the color spectrum from red to green which is from
[255][0][0] to
// [0][255][0]
for (i = 1; i <= 84; i++) {
table[i][0] = table[i - 1][0] - 3;
table[i][1] = table[i - 1][1] + 3;
}
// generate the color spectrum from green to blue which is from
[0][255][0] to
// [0][0][255]
for (i = 86; i <= 169; i++) {
table[i][1] = table[i - 1][1] - 3;
table[i][2] = table[i - 1][2] + 3;
}
// generate the color spectrum from blue back to red which is from
[0][0][255]
// to [255][0][0]
for (i = 171; i <= 255; i++) {
table[i][0] = table[i - 1][0] + 3;
table[i][2] = table[i - 1][2] - 3;
}
// switch the grayscale image to the pseudo color image
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 640; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 420; j++)
image_out[k][i][j] = table[image_in[i][j]][k];
// Write the result image image_out[][]
for (k = 0; k < 3; k++)
for (i = 0; i < 640; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 420; j++)
out.write(image_out[k][i][j]);
} finally {
if ( in != null) { in .close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}Pixel Operators
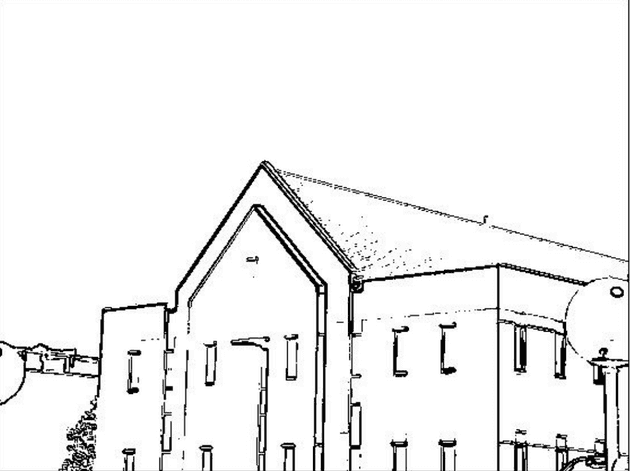
horizontal edge image:
vertical edge image:
gradient image:
thresholded gradient image using a threshold of TE = 128:
Java Solution
import java.io.*;
public class P1 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try { in = new FileInputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/building.raw"); // file
path to read
out = new FileOutputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/building+.raw"); //
file path to write
int i = 0, j = 0;
int[][] image_in = new int[420][560];
int[][] image_out_x = new int[420][560]; // compute the horizontal edge
image
int[][] image_out_y = new int[420][560]; // compute the vertical edge
image
int[][] image_out_g = new int[420][560]; // compute the gradient image
int[][] image_out_g_t = new int[420][560]; // compute the thresholded
gradient image
for (i = 0; i < 420; i++) // here is to read the binary data into
// array image[][]
for (j = 0; j < 560; j++)
image_in[i][j] = in .read();
int x, y; // x is horizontal edge, y is vertical edge
double g; // g is gradient
for (i = 1; i < 419; i++)
for (j = 1; j < 559; j++) {
x = image_in[i + 1][j + 1] - image_in[i - 1][j + 1] + 2 * image_in[i +
1][j] -
2 * image_in[i - 1][j] + image_in[i + 1][j - 1] -
image_in[i - 1][j - 1];
// compute x according the Hpx in Sobel Operators
y = image_in[i - 1][j - 1] - image_in[i - 1][j + 1] + 2 * image_in[i][j - 1] -
2 * image_in[i][j + 1] + image_in[i + 1][j - 1] -
image_in[i + 1][j + 1];
// compute y according the Hpy in Sobel Operators
x = Math.abs(x);
image_out_x[i][j] = x; // put calculated x into the output array
y = Math.abs(y);
image_out_y[i][j] = y; // put calculated y into the output array
g = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);
g = Math.abs(g);
image_out_g[i][j] = (int) g; // put calculated g into the output array
if (g > 128)
image_out_g_t[i][j] = 0; // calculated g with a threshold of Te =
128 and put it into the output
// array
else
image_out_g_t[i][j] = 255;
}
for (i = 0; i < 420; i++) // write out the processed array into the image for
for (j = 0; j < 560; j++) // this one is for the thresholded gradient image
out.write(image_out_g_t[i][j]);
// because it only contains one output stream, so we should write out the
image(horizontal edge image, vertical edge image, gradient image, thresholded gradient image) one by one
} finally {
if ( in != null) { in .close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
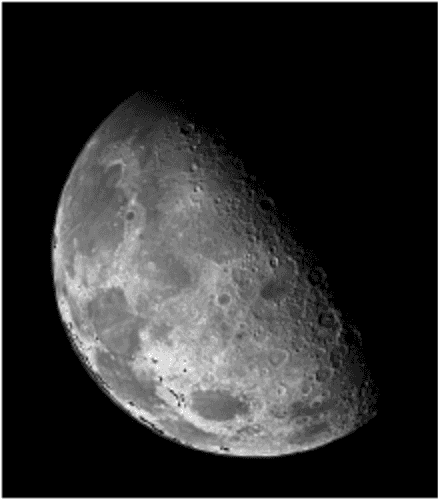
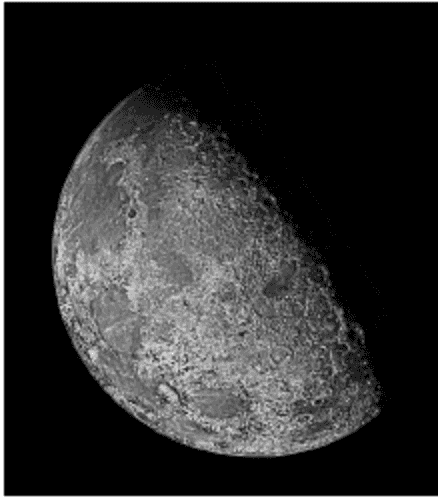
}w=1
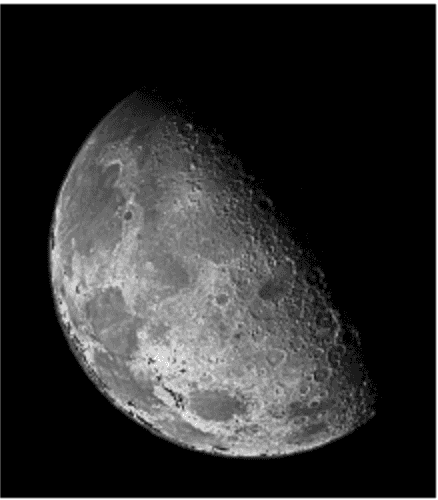
w=2
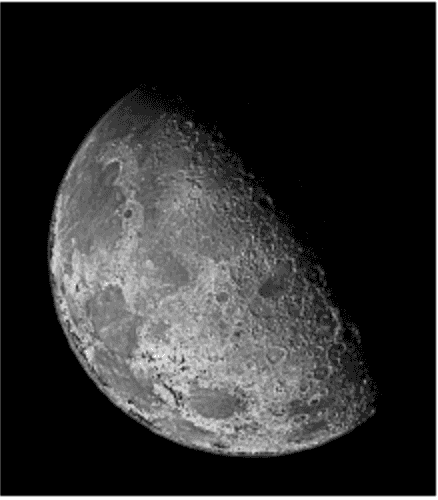
w=3
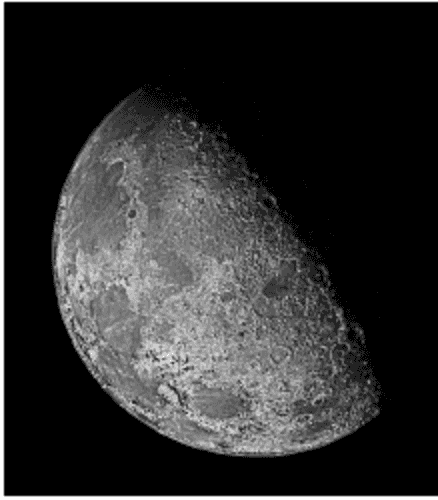
w=4
w=5
Java Solution
import java.io.*;
public class P2 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try { in = new FileInputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/moon.raw"); // file
path to read
out = new FileOutputStream("C:/Users/CHAO/Desktop/moon+.raw"); // file
path to write
int i = 0, j = 0;
int[][] image_in = new int[528][464];
int[][] image_out = new int[528][464];
for (i = 0; i < 528; i++) // here is to read the binary data into
// array image[][]
for (j = 0; j < 464; j++)
image_in[i][j] = in .read();
int w = 1; // w is the coefficient and can be changed to different value for
the test
int s;
int[][] mask = new int[][] {
{0, 1, 0},
{1, -4, 1},
{0, 1, 0}
}; // mask is
the Laplacian sharpening
// filter
for (i = 1; i < 527; i++)
for (j = 1; j < 463; j++) {
s = 0; // s is the sum of the filter
for (int a = -1; a < 2; a++)
for (int b = -1; b < 2; b++) {
s += image_in[i + a][j + b] * mask[1 + a][1 + b]; // filter
the pixel with filter
}
s = image_in[i][j] - w * s; // calculate the new value according to
the
function in the book in
// image sharping with laplacian
sharping filter
image_out[i][j] = Math.abs(s); // s should be the absolute value
before be writen into output array
}
for (i = 0; i < 528; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 464; j++)
out.write(image_out[i][j]);
} finally {
if ( in != null) { in .close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}